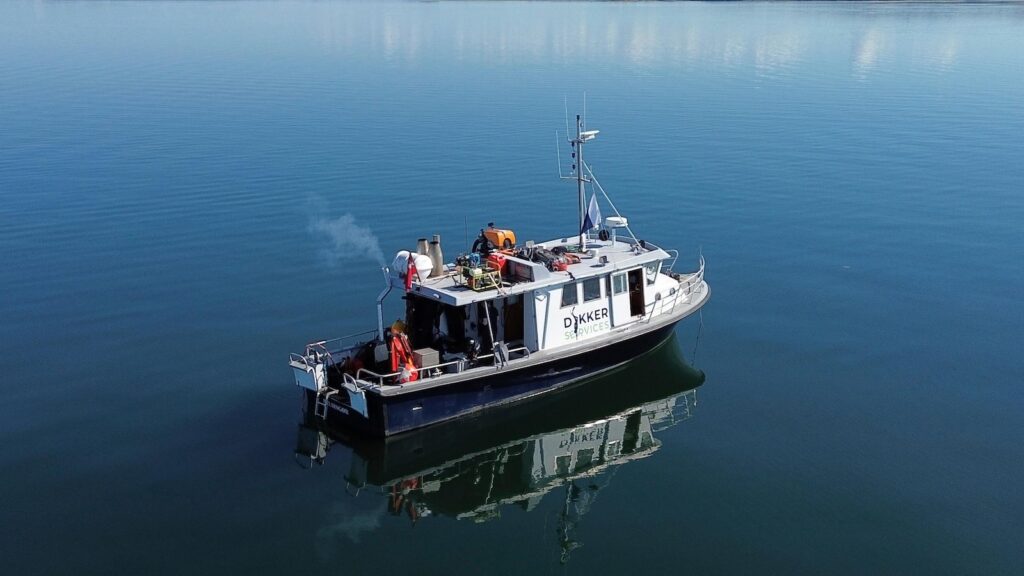
BAY OF AARHUS, Denmark– Listed below the dark blue waters of the Bay of Aarhus in north Denmark, excavators look for seaside negotiations ingested by rising sea levels greater than 8,500 years back.
This summer season, scuba divers came down concerning 8 meters (26 feet) listed below the waves near Aarhus, Denmark’s second-biggest city, and gathered proof of a Rock Age negotiation from the seabed.
It becomes part of a 13.2 million euro ($ 15.5 million) six-year worldwide job to map components of the seabed in the Baltic and North Seas, moneyed by the European Union, that consists of scientists in Aarhus along with from the U.K.’s College of Bradford and the Lower Saxony Institute for Historic Coastal Research Study in Germany.
The objective is to check out sunken North European landscapes and reveal shed Mesolithic negotiations as overseas wind farms and various other sea facilities broaden.
A lot of proof of such negotiations until now has actually been located at places inland from the Rock Age coastline, stated undersea excavator Peter Moe Astrup, that’s leading undersea excavations in Denmark.
” Below, we in fact have an old coast. We have a negotiation that was placed straight at the coast,” he stated. “What we in fact search for out below is exactly how was life at a seaside negotiation.”
After the last glacial epoch, big ice sheets thawed and worldwide water level climbed, immersing Rock Age negotiations and requiring the hunter-gatherer human populace inland.
Concerning 8,500 years back, water level climbed by around 2 meters (6.5 feet) per century, Moe Astrup stated.
Moe Astrup and associates at the Moesgaard Gallery in Højbjerg, simply outside Aarhus, have actually dug deep into a location of around 40 square meters (430 square feet) at the little negotiation they uncovered simply off today’s coastline.
Early dives exposed pet bones, rocks devices, arrowheads, a seal tooth, and a little item of functioned timber, likely a straightforward device. The scientists are brushing the website meter by meter utilizing a sort of undersea vacuum to accumulate product for future evaluation.
They really hope more excavations will certainly discover harpoons, fish hooks or traces of angling frameworks.
” It resembles a time pill,” Moe Astrup stated. “When water level climbed, every little thing was maintained in an oxygen-free setting … time simply quits.”
” We discover entirely unspoiled timber,” he included. “We discover hazelnut. … Every little thing is well maintained.”
Excavations in the fairly tranquil and superficial Bay of Aarhus and dives off the coastline of Germany will certainly be adhered to by later operate at 2 places in the much more unwelcoming North Sea.
The water level surge countless years ago immersed, to name a few points, a huge location called Doggerland that attached Britain with continental Europe and currently exists below the southerly North Sea.
To construct a photo of the fast surge of the waters, Danish scientists are utilizing dendrochronology, the research of tree rings.
Immersed tree stumps maintained in mud and debris can be dated exactly, disclosing when increasing trends sank seaside woodlands.
” We can claim really exactly when these trees passed away at the shorelines,” Moesgaard Gallery dendrochronologist Jonas Ogdal Jensen stated as he peered at an area of Rock Age tree trunk with a microscopic lense.
” That informs us something concerning exactly how the water level altered with time.”
As today’s globe deals with increasing water level driven by climate change, the scientists want to clarify exactly how Rock Age cultures adjusted to moving shorelines greater than 8 centuries back.
” It’s difficult to address specifically what it indicated to individuals,” Moe Astrup stated. “However it plainly had a significant influence over time due to the fact that it entirely altered the landscape.”
Water level climbed by an international standard of around 4.3 centimeters (1.7 inches) in the years approximately 2023.
.