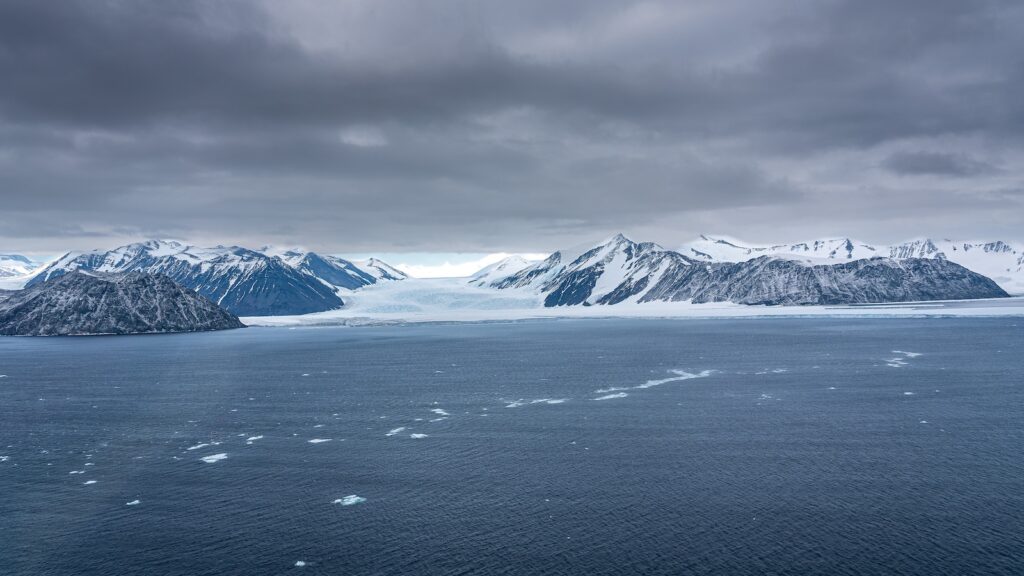
Among one of the most powerful greenhouse gas discharges has actually been uncovered leaking out of splits of the Antarctic seafloor, scientists revealed.
Methane has actually been gauged leaving from gaps in the seabed at a high price as the area warms at extraordinary prices, according to a paper released in Nature Communications.
A big storage tank of methane exists under sea floorings worldwide, which can get away with cracks in the sea flooring, according to the paper.
The unnoticeable gas can be seen in streams of bubbles coming from on the seafloor of Antarctica’s Ross Sea– situated on the north coastline of the continent– stated the scientists, defining the system as “apparently prevalent” throughout the area, instead of a “unusual sensation.”

Robertson Bay in Antarctica.
Traveling Fotoworld/ 500px/Getty Pictures
Various seafloor seeps of liquid and gas were determined in the superficial seaside atmosphere of the Northern Victoria Land and McMurdo Audio– both situated in the Ross Sea– with shipboard water column acoustic studies and From another location Run Automobile studies.
Among one of the most worrying greenhouse gases, methane, has actually been called a “incredibly toxin” by theU.S. Environmental Protection Agency It is accountable for concerning a 3rd of existing anthropogenic international warming and is 25 times a lot more powerful for international warming than co2, according to the agency.
Oceans and shorelines consist of the greatest unpredictabilities of methane launch, according to scientists.
” There is an ongoing void in between the gauged boost in climatic methane and the complete discharges forecasted from presently recognized methane resources,” the writers composed.
The methane leakages show up to happen in locations of the sea that experience infiltration of liquids abundant in hydrocarbons, according to the paper.
Previous research study in the Arctic has actually determined 10s of countless methane seeps– much of them connected to environment modification effects and the deterioration of cryospheric caps, such as antarctic ice, ice and gas hydrates, the writers stated.
Lowering the weight of ice sheets and glaciers in the Arctic has actually been located to reduce hydrostatic stress on subglacial hydrate tanks, which can after that boost subglacial change and methane discharge on the coastline, according to the paper.

Cape Hallett in Antarctica.
Richard Mcmanus/Getty Pictures
Greenhouse gases saved in subsea ice tanks in ice-free areas of the Antarctic are in a similar way prone to environment modification.
Nonetheless, the function of methane discharges in Antarctica has actually not yet been completely established, calling for even more research study in the future, the scientists stated.
” The boosting environment effects in the Antarctic, consisting of the prevalent decrease in ice mass highlights the value of comprehending the existing and future characteristics of liquid and gas launch from the substantial tanks forecasted in the area,” the researchers composed.