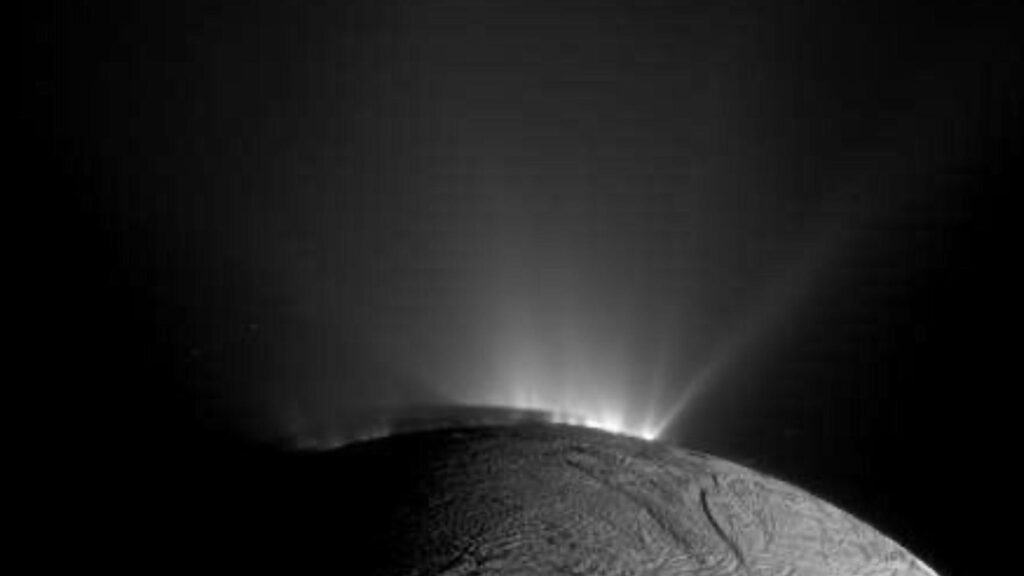
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla.– Researchers have actually revealed brand-new kinds of organics in icy hot springs spouting from Saturn’s moon Enceladus, strengthening the possibility that the ocean world might nurture problems appropriate forever.
Their searchings for, reported Wednesday, are based upon monitorings made by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft in 2008 throughout a close and rapid flyby of Enceladus. The little moon, among 274 orbiting Saturn, has actually long been thought about a prime prospect in the look for life past Planet due to its surprise sea and plumes of water appearing from splits near its south post.
While Enceladus might be habitable, nobody is recommending that life exists.
” Being habitable and being populated are 2 really various points. Our company believe that Enceladus is habitable, however we do not recognize if life is certainly existing,” claimed the College of Washington’s Fabian Klenner, that participated in the research study.
A global group made a decision to release a fresh evaluation of little grains of ice ran into as Cassini flew via the moon’s hot springs. The grains were young compared to the much older hot spring bits that wound up in among Saturn’s outer rings.
These brand-new grains hit Cassini’s planetary dirt analyzer at 40,000 miles per hour (64,800 kph), faster than the old ones. The boosted rate offered a more clear sight of the chemical substances existing, the researchers kept in mind.
Organic particles currently had actually been identified in the old hot spring grains, however their age questioned regarding whether they had actually been changed throughout the years by area radiation.
Researchers located several of the very same particles in the fresh grains, validating they originated from the moon’s below ground sea, in addition to brand-new chemical substances. The searchings for were released in Nature Astronomy.
An ice-encapsulated water globe hardly 310 miles (500 kilometers) throughout with a rough core, Enceladus is presumed of having hydrothermal vents on its sea flooring, rather potentially like those in the Arctic. The moon’s jets of water vapor and icy bits can extend hundreds of miles (kilometers) right into area.
” We are positive that these particles stem from the subsurface sea of Enceladus, boosting its habitability possibility,” the Free College of Berlin’s Nozair Khawaja, the lead writer, claimed in an e-mail.
The researchers prefer brand-new objectives to better check out Enceladus. Released in 1997, Cassini is lengthy gone; the spacecraft was intentionally dived right into Saturn in 2017 following its joint objective by NASA, the European Room Company and the Italian Room Company.
” Having a range of natural substances on an extraterrestrial water globe is merely incredible,” Klenner claimed in an e-mail.
The European Room Company remains in the very early drawing board of a goal to arrive on Enceladus years from currently. China additionally has actually suggested a touchdown objective.
NASA has a spacecraft en course to an additional attracting target to quest for the active ingredients of life: Jupiter’s moon Europa. The Europa Clipper is anticipated to start orbiting Jupiter in 2030 with loads of Europa flybys. ESA additionally has a spacecraft, Juice, that’s headed to Jupiter to check out Europa and 2 various other icy moons that can hold hidden seas.
Below ground seas on moons “are probably the very best prospects for the introduction of extraterrestrial life in our planetary system. This job just validates the requirement for refresher courses,” claimed College of Kent physics teacher Nigel Mason, that was not associated with the most recent searchings for.
___
The Associated Press Health And Wellness and Scientific research Division obtains assistance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Division of Scientific research Education And Learning and the Robert Timber Johnson Structure. The AP is only in charge of all web content