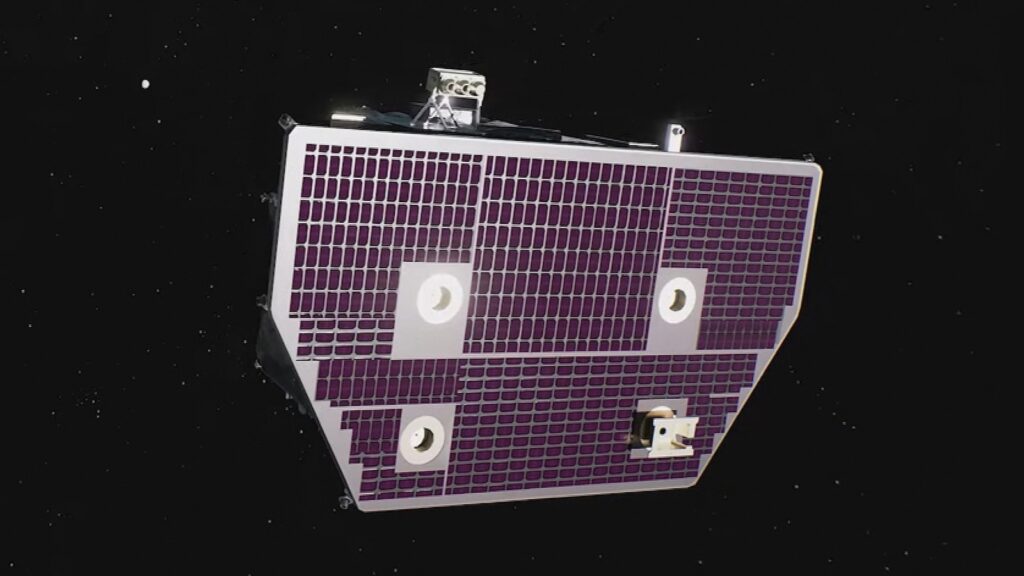
3 satellites are readied to release aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket Wednesday at NASA’s Kennedy Area Facility in Florida, according to a National Aeronautics and Space Administration press release. The goal is to research room climate and its results in the world.
” It is exceptionally immediate for us to in fact recognize what our sunlight is providing for us,” NASA’s head of scientific research, Nicky Fox, informed ABC Information.
She discussed in this goal that NASA will certainly concentrate mostly on astronaut security, while NOAA manages room climate forecasts for private usage in the USA.
” It’s extremely essential for us to recognize what’s originating from the sunlight and exactly how it’s affecting our world,” Fox claimed. “It impacts points like accuracy farming, accuracy exploration, mining, general practitioner signals, spacecraft in orbit, and our astronauts.”
NASA and NOAA start groundbreaking goal to map room climate.
NASA
The goal consists of 3 distinctive satellites, each with special purposes. The SWFO-L1 spacecraft, NOAA’s initial observatory totally committed to room climate monitorings, will certainly act as a very early caution sign for possibly turbulent solar tornados that can impact Planet’s important framework, NASA claimed in a news release.
The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory will certainly research Planet’s uppermost climatic layer.
” This is the very first time we have actually had a system for researching that last border in between Planet’s ambience and room, and considering exactly how that safety layer modifications in action to what’s originating from the sunlight,” Fox discussed.
One more satellite, referred to as IMAP, will certainly determine solar task heading towards Planet and map the heliospheric border – a safety bubble produced by the sunlight.
” It secures every one of the worlds as we are orbiting around the Galaxy,” Fox claimed. “IMAP will certainly have the ability to picture quite high-resolution photos of the border that is safeguarding us from the extreme radiation in interstellar room.”
According to Fox, room climate can impact daily modern technologies like GPS. She discussed that solar task can lower GPS precision, triggering place pens to show up in incorrect settings on maps. Fox contrasted room climate projecting to cyclone monitoring.
” We’re determining criteria that are informing us exactly how extreme a room climate occasion can be.”
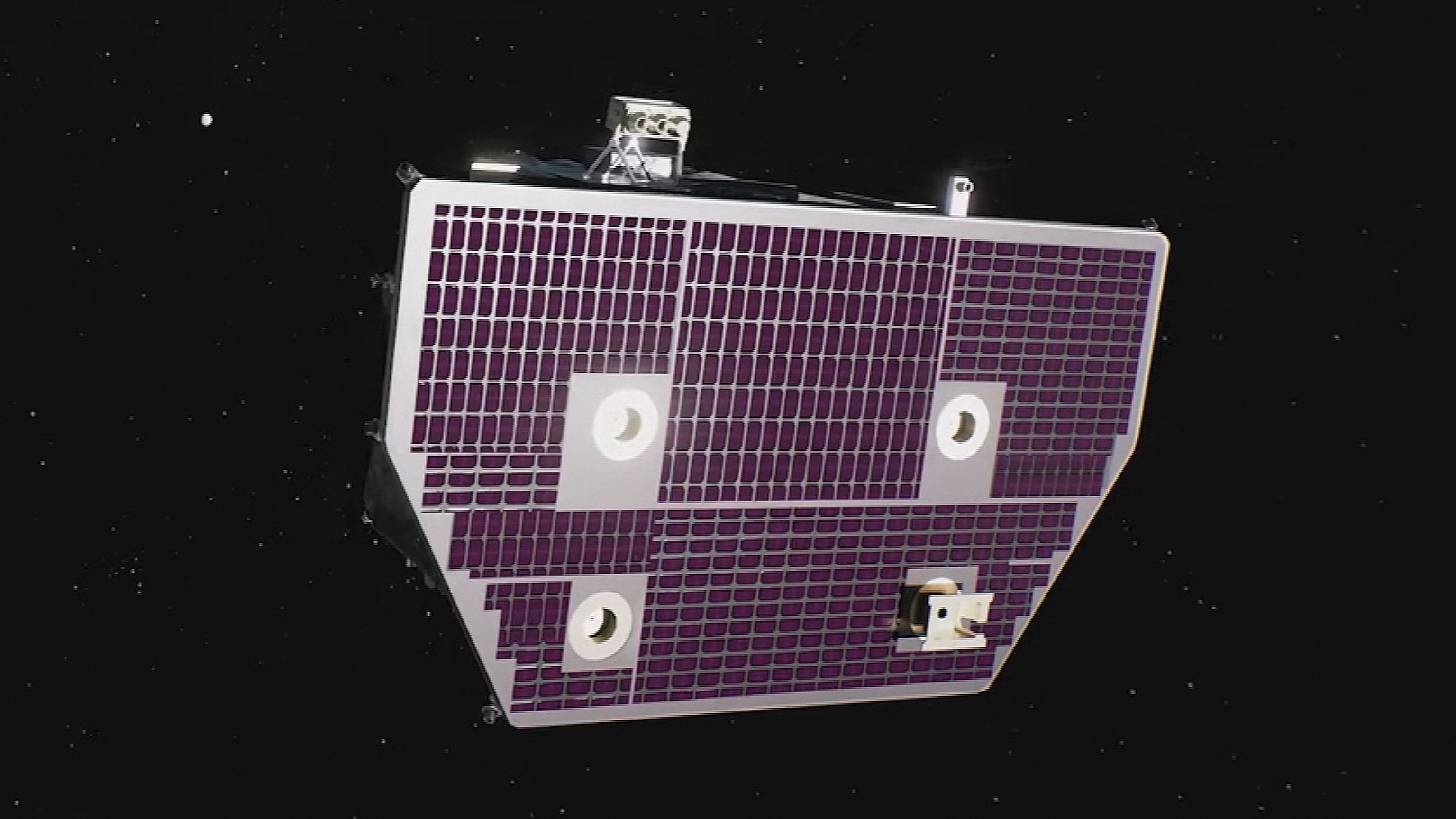
NASA and NOAA start groundbreaking goal to map room climate.
NASA
The satellites will certainly run from what Fox referred to as “the L1 factor,” about one million miles towards the sunlight from Planet.
” They have a really unhampered sight. The Planet does not obstruct. The moon does not enter their means. They have the ability to actually research the sunlight 24/7,” she discussed.
While IMAP has a two-year main goal, Fox noted it has “a great deal of gas and a great deal of capacity to proceed, as long as they’re doing fantastic scientific research.”
” All 3 satellites with each other, we’re sort of considering each and every single component in exactly how the sunlight affects not just Planet however the entire planetary system,” Fox claimed.
The goal likewise links to NASA’s wider study passions.
” As we seek habitable worlds in various other planetary systems … comprehending our celebrity actually aids us recognize the complicated partnership in between a celebrity and a bordering world that can in fact maintain life,” Fox discussed.






