An expanding unique animal profession has preservationists requiring more powerful guidelines to secure the reptiles, birds and various other pets in the wild that are progressively appearing up for sale on web markets and ending up being preferred on social networks.
The two-week Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora is set up to go through Friday in Samarkand, Uzbekistan. A number of propositions associated with the animal profession will certainly be taken into consideration Tuesday.
Individuals have actually recommended tighter guidelines or full restrictions on the profession of a number of varieties consisting of iguanas from the Galapagos Islands, greater than a loads varieties of Latin America arachnids and an odd-looking turtle from Africa.
” What we’re seeing is the animal profession far more considering reptiles, amphibians. Individuals desire uncommon varieties and they do not need to go right into a family pet store,” stated Susan Lieberman, vice head of state for worldwide plan at the not-for-profit Wild animals Preservation Culture. “They go on the internet and there are countless pets, consisting of jeopardized varieties, unlawfully acquired varieties, all offered on the net.”
In the past, the profession was controlled by sales in pet components like elephant ivory andtiger bones Yet Matt Collis, the elderly supervisor of worldwide plan at the International Fund for Pet Well-being, stated real-time pets for the animal profession are progressively showing up on the net.
” The significant development in on-line markets has actually placed customers straight in contact with wild animals investors and bad guys around the globe,” Collis stated. “In today’s culture where practically anything can be acquired with a click of a switch and delivered throughout the globe in an issue of days, no wild animals is risk-free.”
Social media site influencers, that have actually made possessed unique animals cool down, are additionally adding to the trouble, Collis stated.
Numerous of the varieties recommended for higher defense at the CITES meeting remain in Latin America, where an IFAW record in 2015 discovered unlawful profession gets on the increase. The record, covering 18 Spanish talking Latin American nations, states there were greater than 100,000 pets confiscated or poached from 2017 to 2022, with seizures enhancing annually.
The record discovered the real-time animal profession represented an expanding item of the profession, with reptiles standing for around 60% of the pets, while virtually 30% were birds and greater than 10% were amphibians. Several pets were traded in your area or regionally yet there additionally was proof of pets delivered to collection agencies in Europe, Asia and the USA.
Greater Than 90% of the taken wild animals predestined for Europe were real-time pets, validating the need for animals was a vital vehicle driver of the unlawful profession, the record stated.
Amongst the reptile varieties up for tighter profession controls is Home’s Hinged-back Turtle, a seriously jeopardized turtle discovered in West Africa that has an one-of-a-kind depend upon its back enabling it to shut off its back legs and tail.
There are propositions to control the sell 2 vipers varieties native to the island to Ethiopia, 2 varieties of rattlesnake discovered primarily in Mexico, the leaf-tailed gecko from Australia and 2 varieties of sloths from South America, which are progressively showing up in sloth-themed coffee shops in Asia.
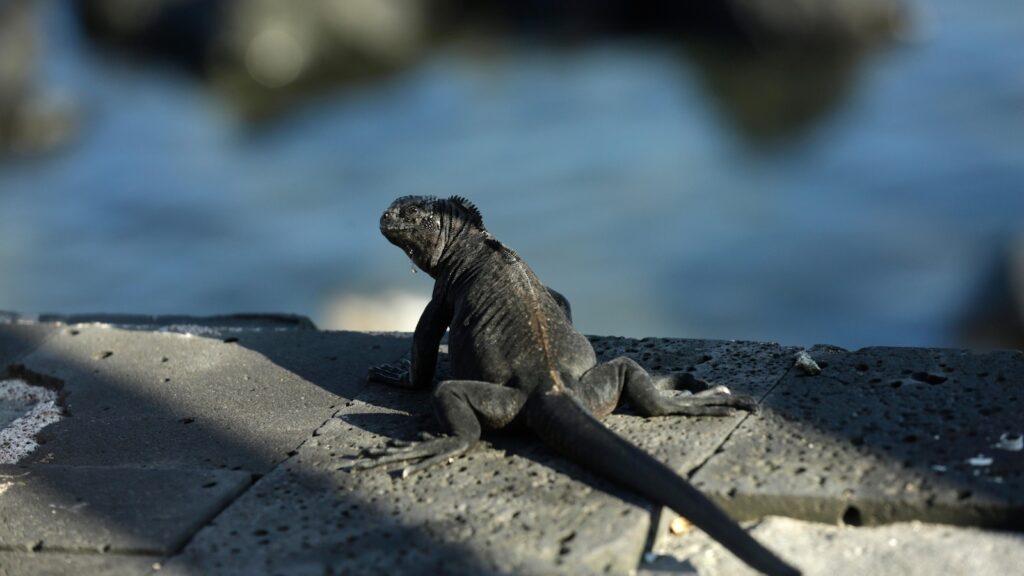
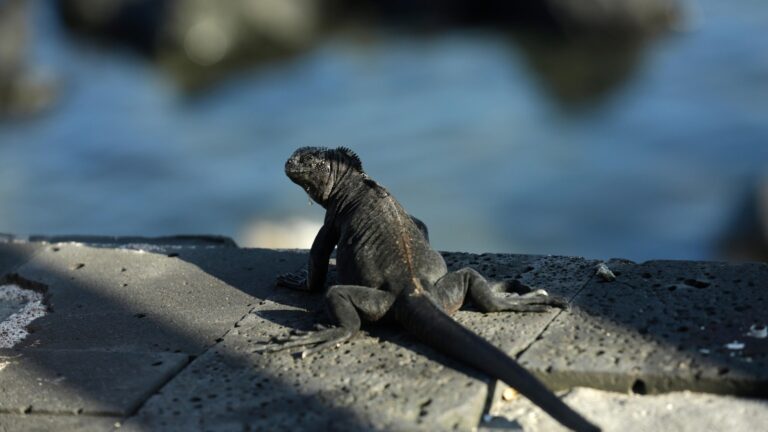
A proposition from Ecuador would certainly outlaw the sell marine and land iguanas from the Galapagos, which are noted by the International Union for Preservation of Nature as seriously jeopardized or prone. There are issues that the unlawful profession might better undercut the populace, which currently encounters dangers from intrusive varieties, climbing tourist and changes in climate connected with the El Nino.
In its CITES proposition, Ecuador stated it does not allow business export of iguanas and accumulating them from the Galapagos has actually been banned for years. Yet Ecuador increased issues that investors are catching and carrying young iguanas by watercraft or overland to ports and averting authorities by mislabeling them as slave reproduced. A lot of the iguanas are predestined for Japan and various other Asia nations and can cost as much $25,000 on the underground market.
The USA sustains the iguana, sloth, viper, turtle and gecko propositions yet is opposed to the rattlesnake listing.
A types can be prohibited for sell its home variety yet marketed on-line by investors that abuse the CITES allowing procedure and restricted reproduction regulations and after that benefit from importing nations that never mind to examine if the pets originated from the wild, Collis stated.
” Theoretically, under mentions regulations, the nations providing those export allows need to be inspecting that these pets, and most importantly their parentage right back to the owner supply, were lawfully obtained in order for an export license to be approved,” Collis stated. “Yet that is not taking place.”
Nations concern allows without validating pet beginnings, which aids traffickers wash pets from unlawful resources, “threatening the extremely structure suggested to secure these varieties,” he stated.
The mentions propositions accentuate a long-running trouble with restricted reproduction of unique varieties, according to Lieberman of the Wild Animals Preservation Culture.
” When the treaty was prepared in the very early 1970s, there had not been a great deal of restricted reproduction and individuals believed, ‘Well, if they’re reproduced in bondage, it’ll take stress off the wild,” she stated. “Seems excellent, other than it does not function by doing this. Reproducing in bondage additionally develops a market, yet they’re less expensive from the wild. And additionally it’s a terrific method to wash.”
A proposition has actually additionally been sent at the convention to control the sell greater than a loads varieties of arachnids. Bolivia, Argentina and Panama note they are “amongst one of the most greatly traded teams of invertebrates” with over half all varieties offered online. The proposition would certainly allow the sell the crawlers as long as there is evidence the resources are lawful, lasting and deducible.
” Some arachnid varieties are specifically prone to overexploitation because of their lengthy life expectancy, minimal geographical variety and reduced reproductive price,” according to the proposition. “Amazingly, a lot of them are not managed globally, in spite of the high schedule of numerous varieties in worldwide profession.”
The USA Organization of Reptile Keepers opposes the arachnid listing, which it called “inconsistent” for rolling several varieties right into a solitary proposition.
The organization, which promotes for liable exclusive possession and sell reptiles and amphibians, recommended various other reptile propositions show federal government overreach, keeping in mind the extended modifications to iguana sales are unneeded considering that present guidelines “supply ample defense.”
” Many varieties have actually restricted sell slave reproduced samplings which is not a risk to wild populaces,” David Garcia, the company’s lawful advice and its delegate at the CITES meeting, stated in a declaration. “Regrettably, several nations, teams, and people take the ridiculous setting that the method to restrict dangers to wild populaces is to make the restricted recreation of those varieties harder.
Yet a record from the not-for-profit Facility for Organic Variety, shown The Associated Press and because of be launched Dec. 8, discovered that the USA was amongst the most significant markets for the animal profession, importing usually 90 million real-time amphibians, arachnids, birds, tropical fish, creatures and reptiles yearly.
” Wild animals exploitation, consisting of for the animal profession, is a significant vehicle driver of the worldwide termination dilemma,” the record stated. “One million varieties get on track to encounter termination in coming years unless activity is required to deal with varieties loss. Dealing With the USA’ duty in the unique animal profession have to be a leading concern to stem this dilemma and secure biodiversity for future generations.”