WASHINGTON– Our hands can expose a great deal concerning exactly how an individual has actually lived– which holds true for very early human ancestors, as well.
Various tasks such as climbing up, realizing or hammering area stress and anxiety on various components of our fingers. In action to duplicated stress and anxiety, our bones have a tendency to enlarge in those locations.
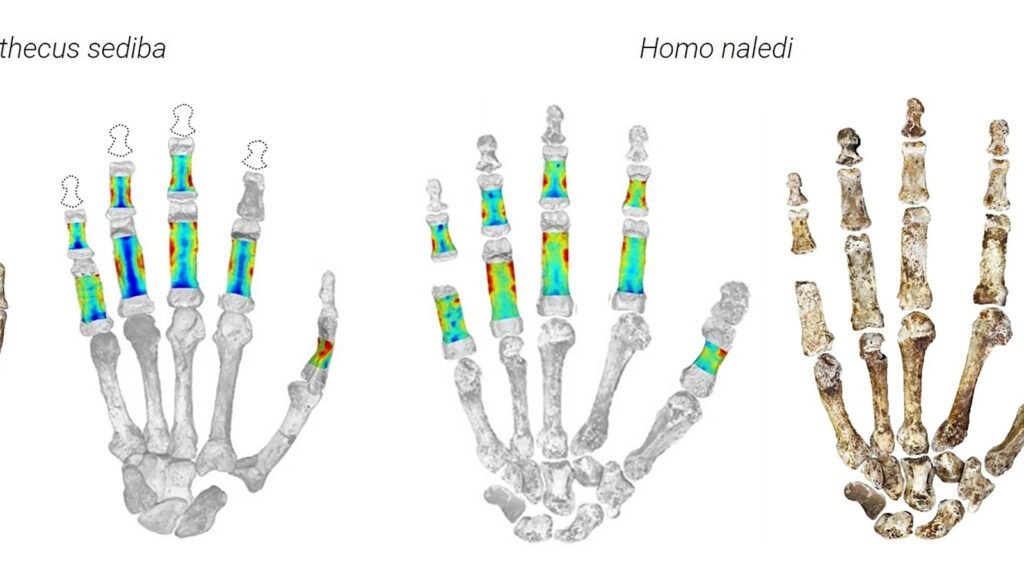
To research exactly how ancient humans utilized their hands, researchers made use of 3D scanning to determine and evaluate the bone density of fingers.
They concentrated on the fossil hands of 2 very early human forefather varieties recouped from excavations in southerly Africa, called Australopithecus sediba and Homo naledi. The people lived around 2 million years earlier and about 300,000 years earlier, specifically.
Both old human varieties revealed indications of all at once utilizing their hands to walk around– such as by climbing up trees– along with to realize and adjust things, a need to being able to make devices.
” They were most likely strolling on 2 feet and utilizing their hands to adjust things or devices, however likewise hung around climbing up and hanging,” maybe on trees or high cliffs, stated research study co-author and paleoanthropologist Samar Syeda of the American Gallery of Nature.
The research study was published Wednesday in Scientific Research Advancements.
The searchings for reveal there had not been a basic “development in hand feature where you begin with even more ‘ape-like’ and wind up a lot more ‘human-like,'” stated Smithsonian paleoanthropologist Rick Potts, that was not associated with the research study.
Total fossil hands are reasonably unusual, however the samplings made use of in the research study provided a possibility to comprehend the family member pressures on each finger, stated Chatham College paleontologist Erin Marie Williams-Hatala, that was not associated with the research study.
” Hands are just one of the main methods we involve with globe around us,” she stated.
___
The Associated Press Wellness and Scientific research Division obtains assistance from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Scientific research and Educational Media Team and the Robert Timber Johnson Structure. The AP is exclusively in charge of all web content.