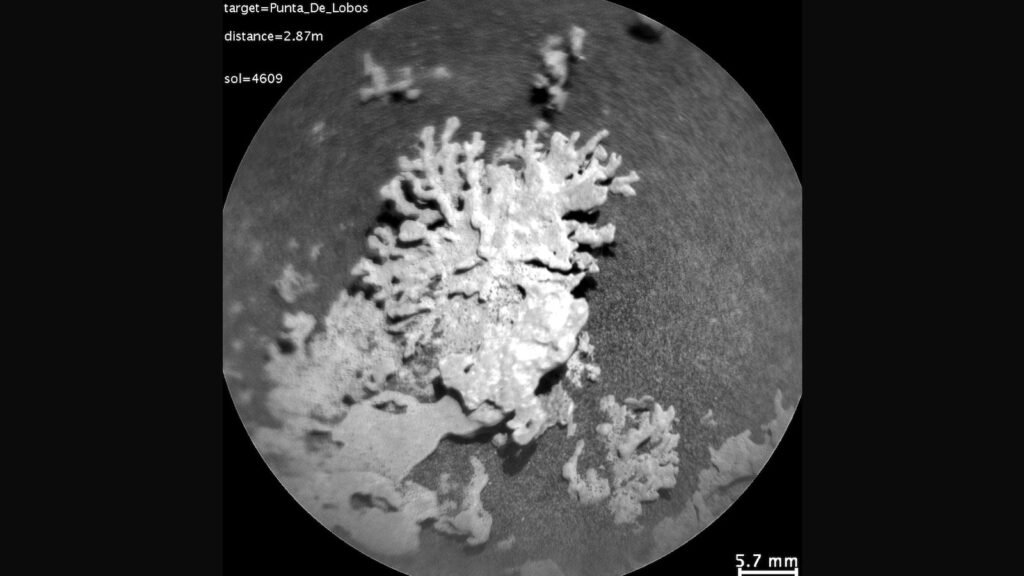
NASA has actually recorded a photo of a coral-like rock on Mars approximated to be a number of billions of years of ages.
The room company’s Interest Wanderer returned pictures of a tiny, wind-eroded rock that looks like an item of reef on July 24– the 4,609 th Martian day of the wanderer’s objective. The rock has to do with an 1 inch vast.
The Interest Wanderer has actually recorded several pictures of this sort of rock, according to NASA.
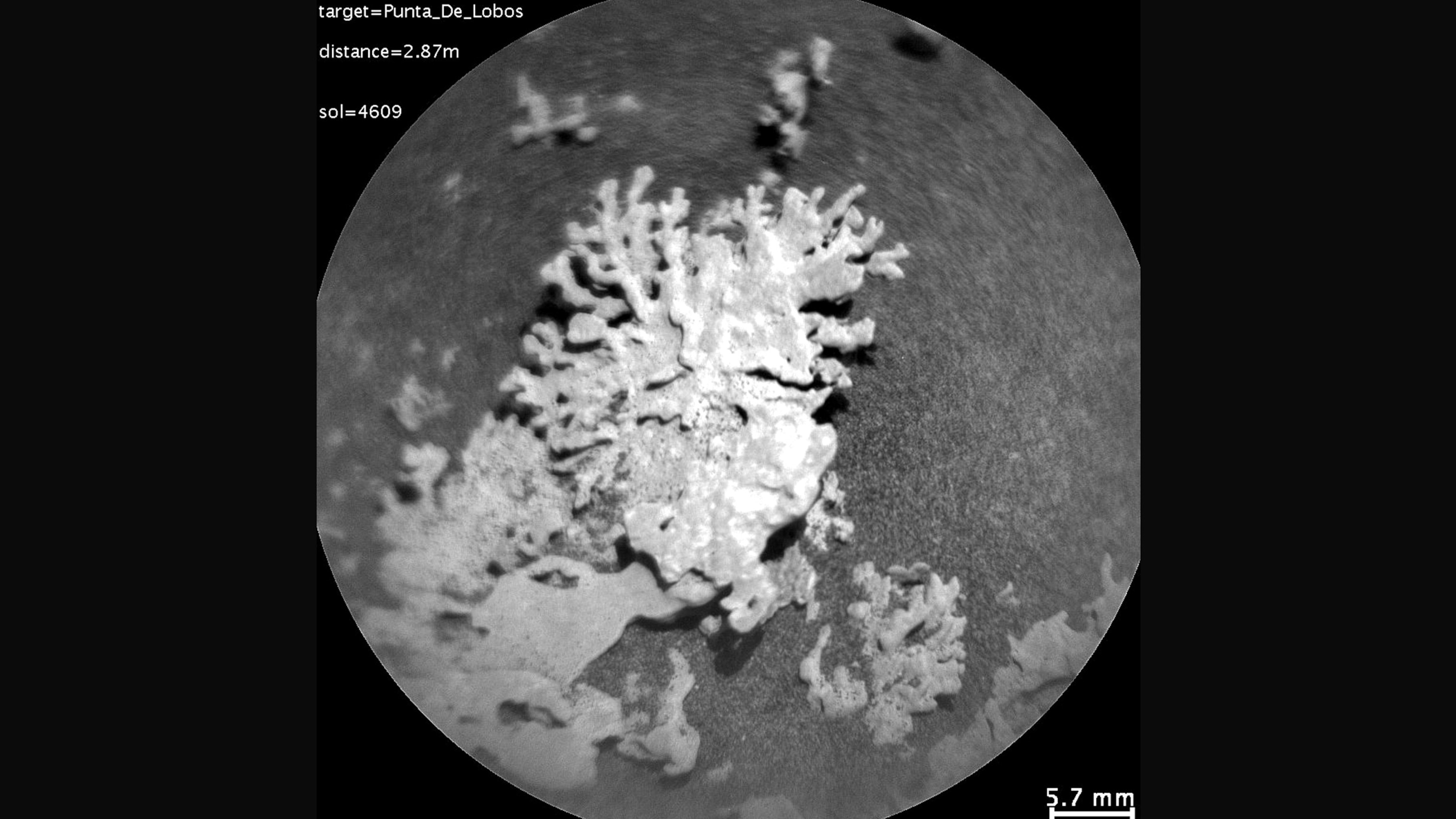
NASA’s Interest Mars wanderer utilized the Remote Micro Imager, component of its ChemCam tool, to watch this wind-eroded rock formed like an item of reefs on July 24, 2025.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/LANL/ CNES/CNRS/IRAP/ IAS/LPG
When fluid water still fed on Mars, it brought liquified minerals right into rock fractures, NASA stated. When the fluid dried out, it left the solidified minerals behind. The “one-of-a-kind forms” left today were formed by sandblasting over billions of years, NASA stated.
An oddly designed 2-inch rock nicknamed “Paposo” was likewise uncovered on July 24.
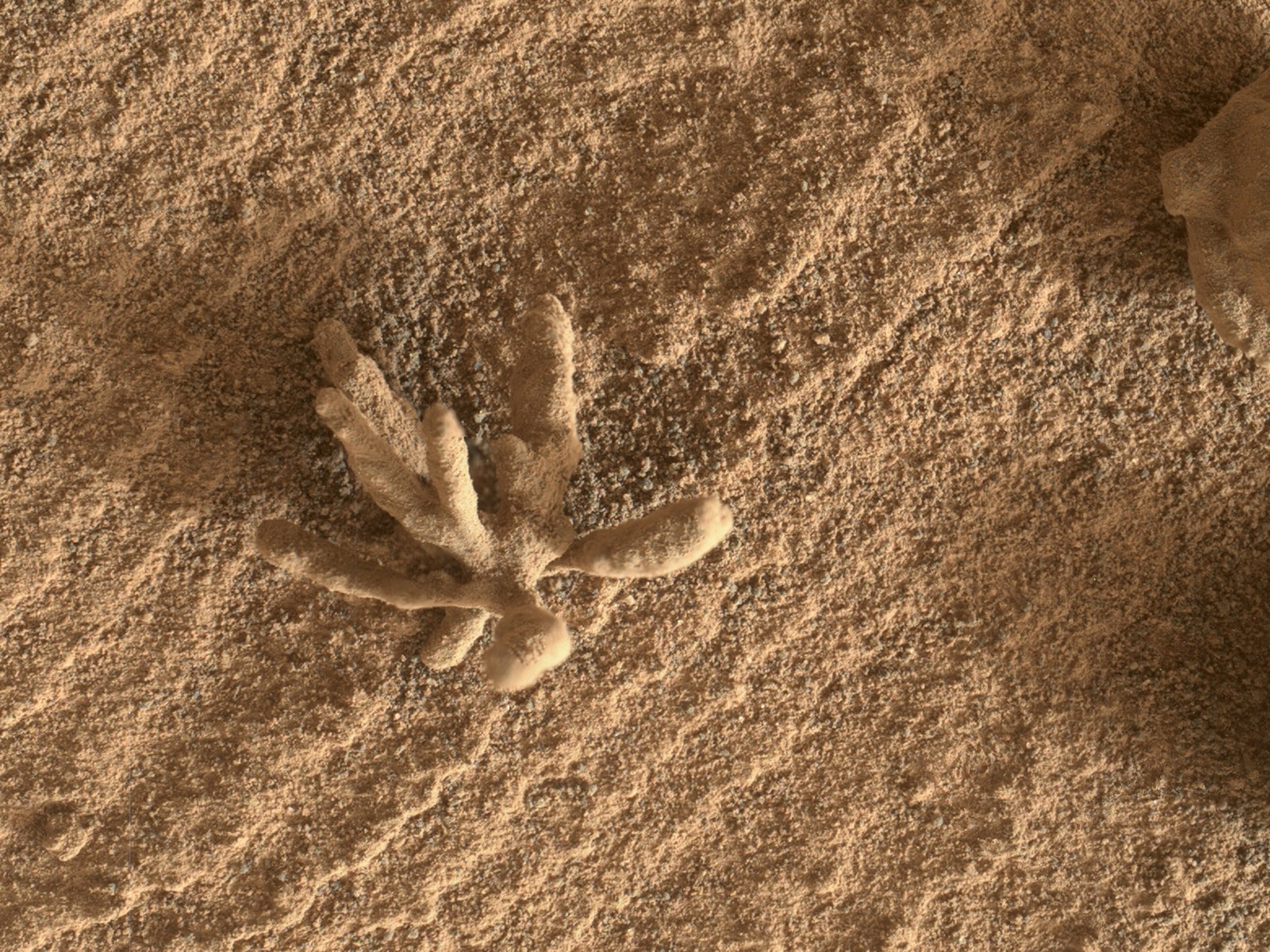

Smaller sized than a dime, the flower-like rock artefact left wing was imaged by NASA’s Interest Mars wanderer utilizing its Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) video camera on completion of its robot arm. The picture was tackled Feb. 24, 2022.
NASA
One More flower-shaped rock was discovered in 2022.
The blossom rock is likewise believed to have actually developed when mineralizing liquids took a trip via avenues in the rock, according to NASA.
The Interest Wanderer was developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Research laboratory, which is leading the objective on Mars.
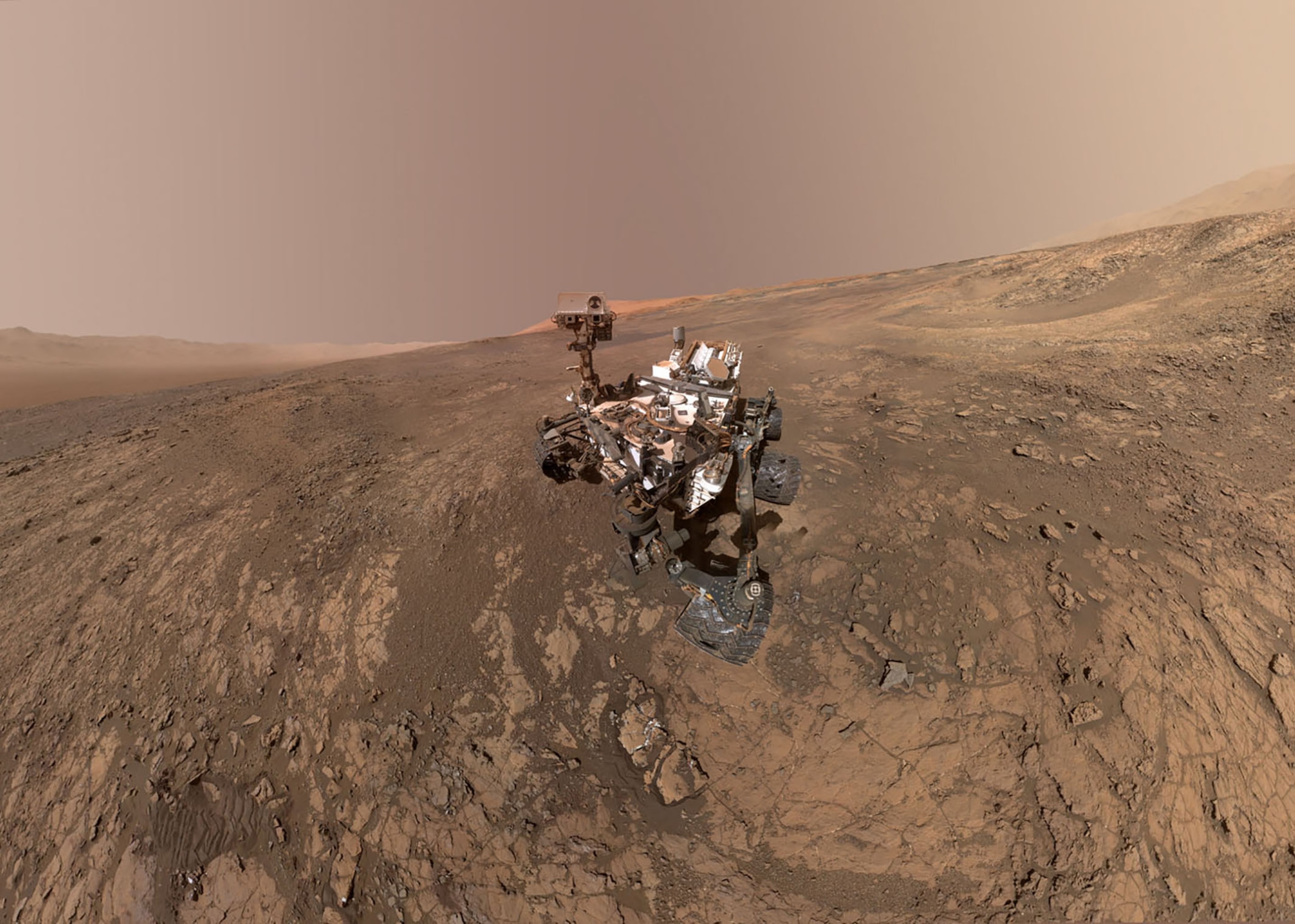

This NASA picture tackled Feb. 4, 2018, is a self-portrait of NASA’s Interest Mars wanderer on Vera Rubin Ridge. Straight behind the wanderer is Wind Crater’s edge.
NASA
Interest came down on Mars in 2012 after an eight-month, 352-million-mile trip. It was the biggest and most qualified wanderer ever before sent out to the Red World at the time, according to NASA.
The wanderer discovered chemical and mineral proof of previous habitable atmospheres on Mars early in its objective and has actually checked out concerning 22 miles of the earth.
Interest remains to gather examples and collect information from a time when the earth can have been home to microbial life, according to NASA.





